React Native 0.82 - New Architecture Only
Today we're excited to release React Native 0.82: the first React Native that runs entirely on the New Architecture.
This is a milestone release for React Native and we believe it's the start of a new era. In future versions we will be removing the remaining code from the Legacy Architecture to reduce install size and streamline the codebase.
In addition, 0.82 also ships with experimental opt-in to a newer version of Hermes called Hermes V1. We’re also enabling several React features by updating the React version to 19.1.1, and shipping support for DOM Node APIs.
Highlights
Highlights
New Architecture Only
In React Native 0.76 we announced that The New Architecture became the default architecture of React Native.
Since then, the New Architecture has been tested and refined and we're confident in making it the only architecture for this and future versions of React Native.
This means that if you try to set newArchEnabled=false on Android, or if you try to install CocoaPods with RCT_NEW_ARCH_ENABLED=0 on iOS, these will be ignored and your app will still run using the New Architecture.
How to migrate
If you haven’t migrated your project to the New Architecture, we recommend first migrating your project to React Native 0.81 or Expo SDK 54. These are the last versions that allow you to use the Legacy Architecture. They contain warnings and performance improvements specifically to help migrating to the New Architecture.
Then enable the New Architecture in 0.81 and verify that your application is working fine.
Once you're using the New Architecture in 0.81, you can update safely to React Native 0.82 which prevents enabling the Legacy Architecture.
If an incompatible 3rd party dependency is blocking you from migrating to the New Architecture, we recommend you reach out to the library maintainers directly.
If a bug in React Native core is blocking you from migrating, we recommend you reach out to us through our issue tracker.
Interop Layers & 3P library compatibility
We will keep the interop layers in the codebase for the foreseeable future. All the classes and functions that are required by the interop layers won’t be removed anytime soon. We will share further updates in the future regarding the removals of Interop Layers.
We’ve also verified that the 3P libraries that offer backward compatibility with both legacy and New Architectures will keep on working with 0.82 where New Architecture is the only architecture.
Removal of Legacy Architecture classes
To ensure backward compatibility and reduce breaking changes, we are not removing any APIs of the Legacy Architecture from the core of React Native in this version. Removing the Legacy Architecture will allow us to save significant size on the overall bundle size, therefore the removal is scheduled to start from the next version of React Native.
You can find more information in RFC0929: Removal of the Legacy Architecture of React Native.
Experimental Hermes V1
React Native 0.82 adds support for opting into Hermes V1.
Hermes V1 is the next evolution of Hermes. We've been experimenting with it internally in our apps, and it is now time for the community to try it as well. It comes with improvements in the compiler and in the VM that boost Hermes performance.
From initial tests and benchmarks, Hermes V1 outperforms current Hermes in various scenarios. We have seen improvements in bundle loading and TTI. The improvements strongly depend on the details of your apps.
On the Expensify app, a real world and complex application, we have seen the following improvements:
| Metric | Android (low end device) | iOS |
|---|---|---|
| Bundle Load Time | 3.2% faster | 9% faster |
| Total TTI | 7.6% faster | 2.5% faster |
| Content TTI | 7.2% faster | 7.5% faster |
For Total TTI, we measured the time it takes from bundle loading to when the first screen in the app is rendered and it is interactive.
For Content TTI, we measured the time it takes for a component to be interactive, starting from the first rendering of the component itself.
Hermes V1 does not yet contain JS-to-native compilation (previously known as “Static Hermes”) or the JIT compilation that was presented during React Native EU 2023. We are still testing these features, and will share more as we make progress.
How to enable Hermes V1
While Hermes V1 is in the experimental phase, you’ll need to build React Native from source to try it out. Once Hermes V1 ships as default in a future React Native version, this restriction will be lifted.
To try Hermes V1 in your own project, use the following steps:
- Force your package manager to resolve the experimental version of Hermes V1 compiler package by modifying the corresponding section of your
package.jsonfile (note that the current versioning convention is only for the experimental phase of Hermes V1):
- yarn
- npm
"resolutions": {
"hermes-compiler": "250829098.0.1"
}
"overrides": {
"hermes-compiler": "250829098.0.1"
}
- Enable Hermes V1 for Android by adding
hermesV1Enabled=trueinside theandroid/gradle.propertiesfile, and configure React Native to build from source by editingandroid/settings.gradle:
- android/gradle.properties
- android/settings.gradle
+ hermesV1Enabled=true
+ includeBuild('../node_modules/react-native') {
+ dependencySubstitution {
+ substitute(module("com.facebook.react:react-android")).using(project(":packages:react-native:ReactAndroid"))
+ substitute(module("com.facebook.react:react-native")).using(project(":packages:react-native:ReactAndroid"))
+ substitute(project(":packages:react-native:ReactAndroid:hermes-engine")).using(module("com.facebook.hermes:hermes-android:250829098.0.1"))
+ }
+ }
- Enable Hermes V1 for iOS by installing pods with
RCT_HERMES_V1_ENABLED=1environment variable.
RCT_HERMES_V1_ENABLED=1 bundle exec pod install
Keep in mind that Hermes V1 is not compatible with the precompiled React Native builds, so make sure you don’t use the RCT_USE_PREBUILT_RNCORE flag when installing pods.
- To verify whether the app is running Hermes V1, you could run the following in your JavaScript code or DevTools console:
HermesInternal.getRuntimeProperties()['Static Hermes'] === true;
React 19.1.1
This release of React Native ships with the latest React stable: React 19.1.1.
This release of React contains full support for owner stacks for React Native. Back in React Native 0.80, when we shipped support for 19.1.0, we mentioned that owner stacks were not fully supported if you were using the @babel/plugin-transform-function-name Babel plugin. This release lifts this restriction and enables owner stacks for all React Native users.
| BEFORE | AFTER |
|---|---|
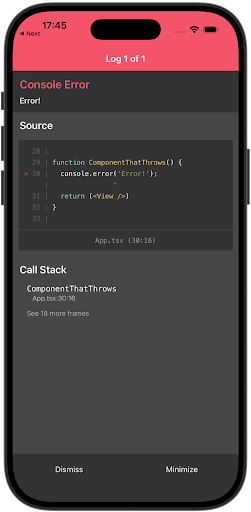 | 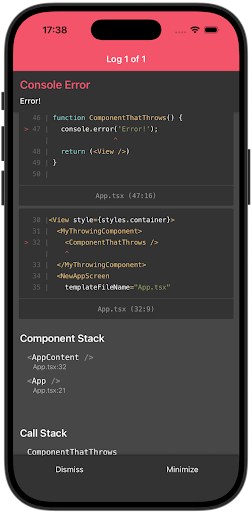 |
React 19.1.1 also improves the reliability of useDeferredValue and startTransition in a Suspense boundary for React Native. These are essential React features, designed to boost app responsiveness. Previously both were wrongly showing the fallback component when used together with a Suspense boundary on React Native. With React 19.1.1, they now consistently perform as expected on React Native, aligning their behavior with Web.
DOM Node APIs
Starting from React Native 0.82, native components will provide DOM-like nodes via refs.
Before, native components provided React Native-specific objects with just a handful of methods like measure and setNativeProps. After this release, they will provide nodes implementing a subset of the DOM API that allow traversing the UI tree, measuring layout, etc. as they do on Web, e.g.:
function MyComponent(props) {
const ref = useRef();
useEffect(() => {
const element = ref.current;
// New methods
element.parentNode;
element.parentElement;
element.childNodes;
element.children;
const bounds = element.getBoundingClientRect();
const doc = element.ownerDocument;
const maybeElement = doc.getElementById('some-view');
// Legacy methods are still available
element.measure((x, y, width, height, pageX, pageY) => {
/* ... */
});
}, []);
return <View ref={ref} />;
}
Additionally, this will expose access to leaf text nodes (created by the Text component) and document nodes representing React Native root nodes.
This is a backwards compatible change, as the new nodes will continue implementing the legacy methods (like measure).
For more information, please check our documentation.
Other changes
Web Performance APIs (Canary)
React Native now implements a subset of the performance APIs available on Web:
- High Resolution Time: defines
performance.now()andperformance.timeOrigin. - Performance Timeline: defines
PerformanceObserverand methods to access performance entries in the performance object (getEntries(),getEntriesByType(),getEntriesByName()). - User Timing: defines
performance.markandperformance.measure. - Event Timing API: defines
evententry types reported toPerformanceObserver. - Long Tasks API: defines
longtaskentry types reported toPerformanceObserver.
They allow tracking different aspects of performance in your app at runtime (for telemetry) and they will be visible in the performance panel in React Native DevTools (available in a future version of React Native).
They are currently available only in the canary release level, and will be released as stable in a future version of React Native.
Create a debugOptimized build type for Android
Starting with React Native 0.82, you will be able to use the debugOptimized build type to speed up your development experience.
Historically, Android creates two default build variants:
debug, used by default when developing and that allows you to connect to the various debugger tools such as React Native DevTools, Metro, the Android JVM and C++ debuggerrelease, used when shipping your application to production. This is fully optimized, with obfuscation and optimization that will make debugging harder.
As most React Native developers won’t need to use the C++ debugger when developing, we introduced the debugOptimized build type.
With debugOptimized your animations and re-rendering will be faster, because you’re running a React Native build with several C++ optimizations enabled. At the same time you will still be able to use React Native Dev Tools to debug your JavaScript code.
When using debugOptimized, you won’t be able to use the C++ native debuggers, but you will still be able to use it if you use the debug build type.
To run the debugOptimized variant for your app built with the Community CLI you can invoke:
- Raw React Native
- Expo
npx react-native run-android --mode debugOptimized
npx expo run:android --variant debugOptimized
The debugOptimized build type has also been backported to React Native 0.81 and Expo SDK 54.
You can see the debugOptimized in action in these samples where we’re rendering several animations on screens.
The build running debug is running at ~20FPS while the debugOptimized one is running at ~60FPS:
debug | debugOptimized |
|---|---|
 |  |
Breaking Changes
Uncaught promise rejections will now raise console.error
Following the improvement of reporting uncaught JavaScript errors in the previous version, we will now be reporting uncaught promises through that mechanism as well:
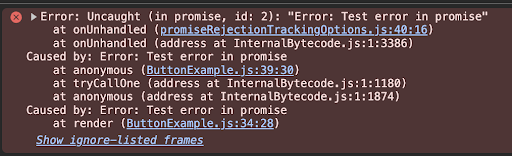
Due to a bug, these were completely swallowed and ignored previously, so please expect some pre-existing errors to surface after upgrading to React Native 0.81. For that reason, previously pre-existing errors might also surface in JavaScript errors reported to your backend, and create a surge in new reports.
Other Breaking Changes
General
- Move
ReactNativeFeatureFlagstosrc/private- In general you should not depend on
ReactNativeFeatureFlagsat all as that is a private API.
- In general you should not depend on
- Type of
Appearance.setColorScheme()has been updated to no longer accept a nullable value- Use 'unspecified' instead of null/undefined in the edge case that the color scheme needs to be reset.
iOS
- Migrated
RCTDisplayLinkaway from legacy apiRCTModuleDataas we plan to remove it in the future.
Android
- Class
com.facebook.react.bridge.JSONArgumentsis removed as was accidentallypublic - Deprecate
MessageQueueThreadPerfStats- We deprecated this API and replaced it with stub. You should not rely on stats from this API anymore as the provided stats were not reliable
- Bump Gradle from 8.x to 9.0.0
- List of all the changes in the next major stable version of Gradle 9.0.0 is available here but we expect no impact at all to users
C++
- Delete backward compatibility headers for
CallbackWrapper.h/LongLivedObject.h- The correct include for those headers is
#include <react/bridging/LongLivedObject.h>and#include <react/bridging/CallbackWrapper.h>. - You should not use the old includes under
#import <ReactCommon/….h>
- The correct include for those headers is
Read the full list of breaking changes in the CHANGELOG for 0.82.
Acknowledgements
React Native 0.82 contains over 868 commits from 93 contributors. Thanks for all your hard work!
We want to send a special thank you to those community members that shipped significant contributions in this release:
- Dawid Małecki and Jakub Piasecki for the help in rolling out Hermes V1.
- Krystof Woldrich for the support with fixing the swallowing of uncaught promise rejections.
- Riccardo Cipolleschi for the support with writing the React 19.1.1 and Hermes V1 paragraph above.
- Rubén Norte for the support with writing the DOM API and Performance API paragraphs.
- Tomasz Zawadzki for the support with the
debugOptimizedbenchmarking.
Upgrade to 0.82
Please use the React Native Upgrade Helper to view code changes between React Native versions for existing projects, in addition to the Upgrading docs.
To create a new project:
If you use Expo, React Native 0.82 will be available as part of the expo@canary releases.
The next SDK, SDK 55, will be shipped with the next stable release of React Native: 0.83.
0.82 is now the latest stable version of React Native and 0.79.x moves to unsupported. For more information see React Native's support policy.



